

The first two endpoints have a priority of 1. The TTL for each record is one hour (3600 seconds). _minecraft._ 3600 SRV 5 .Īs we've already seen, the service name is "_minecraft", and the protocol is "_tcp". The SRV record set for the Minecraft servers for might look like this: _minecraft._ 3600 SRV 5. Putting these values together, the query name to discover the Minecraft servers would be _minecraft._. For Minecraft, the first label is "_minecraft" and the second label is "_tcp". The application protocol specifies the service and protocol values in the query name. To find the set of endpoints for a service that uses SRV records, a client sends a DNS query of type SRV for a query name in the format _Service._Protocol.Name. The IANA registry includes whether TCP or UDP is supported and a default port number. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) now maintains an official registry of service names. Service names were first collected in a temporary registry operated by.
Many applications have used SRV records over the years. The same value can be used for all weights if the service owner wants equal load balancing. The same load balancing would be achieved if the weight values were 10 and 90 because weights are relative. If the result is 101 through 1000, the second endpoint would be used. If the result is 1 through 100, the first endpoint would be used. If two SRV records have the same priority value and weight values of 100 and 900, a client would generate a random number between.

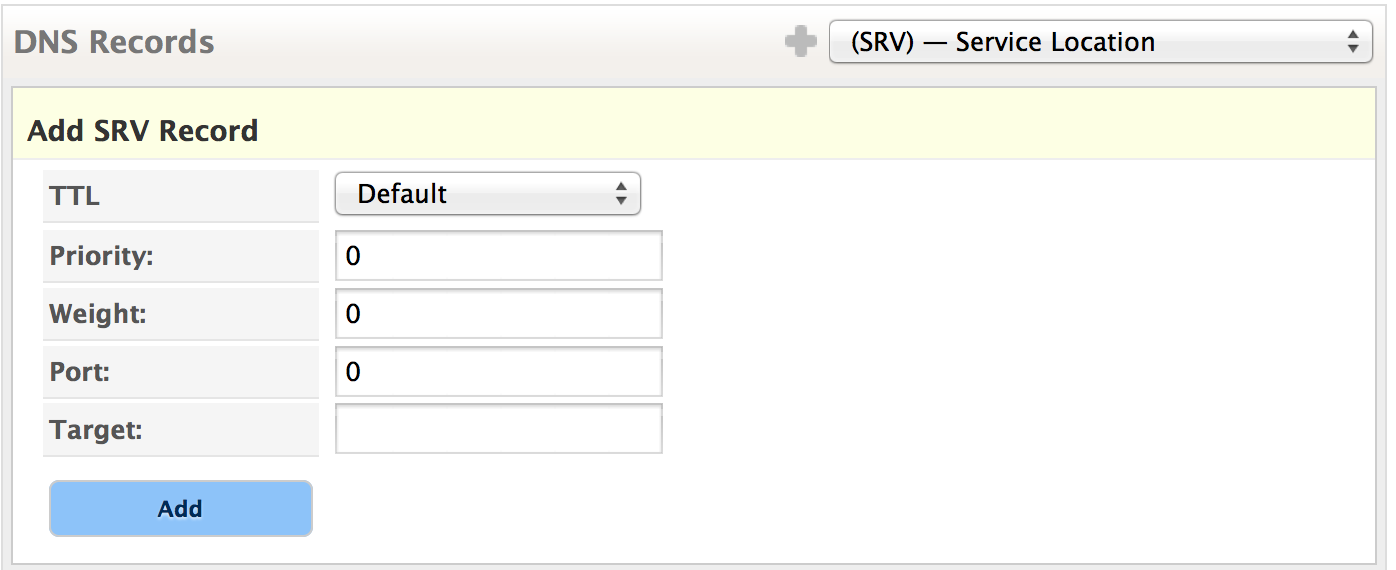
The client adds the weight values and generates a random number between 1 and the sum of the weights to select an endpoint. Weight specifies the relative amount of requests that each endpoint with the same priority should receive.Ĭlients randomly select one of the endpoints using their weights if multiple SRV records have the same priority. The endpoints with the lowest priority are used first. But SRV also includes a random component through the weight field for more dynamic load balancing. Priority is similar to the preference field in MX records. Priority and weight determine how clients select one of the endpoints in a set of SRV records. The target may resolve to a CNAME record.
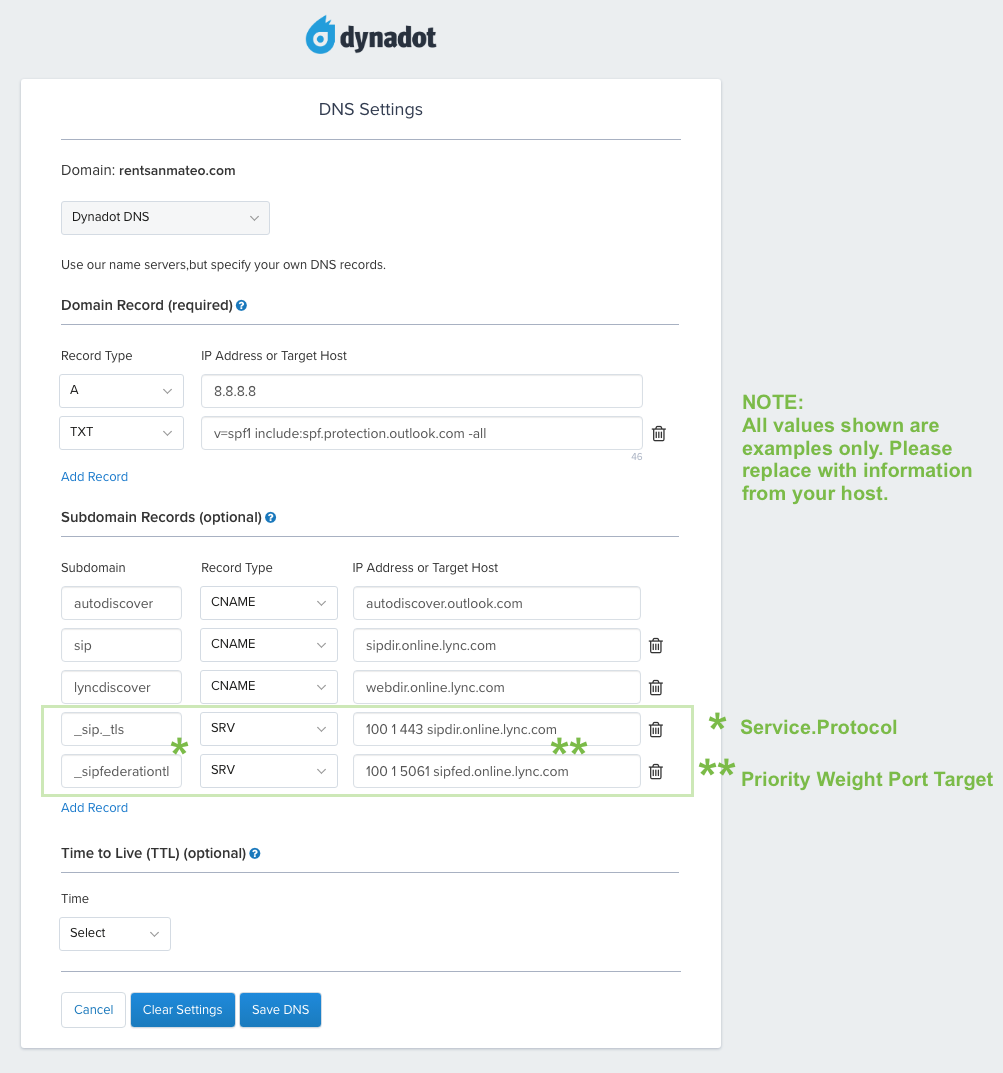
The SRV record type was proposed in the late 1990s in RFC 2782. SRV also provides a load balancing feature. SRV records allow services to be advertised on specific ports and used in an order controlled by the owner of the service. The SRV or "service locator" DNS record type enables service discovery in the DNS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
